

By Dr Bill Eccles, Bolt Science
You may have come across before a vague statement that joints consisting of long bolts are superior to those having short bolts. Or, more technically, a joint grip length to bolt diameter ratio of four or more is advisable. So why are long bolts to be preferred over short bolts?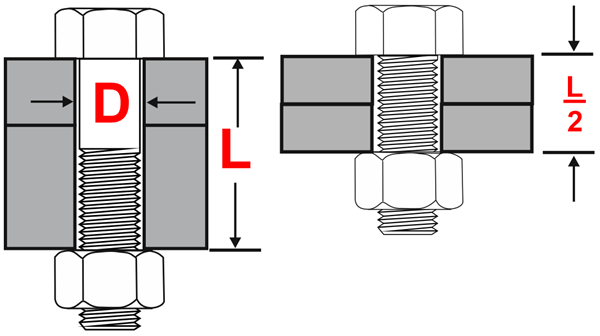
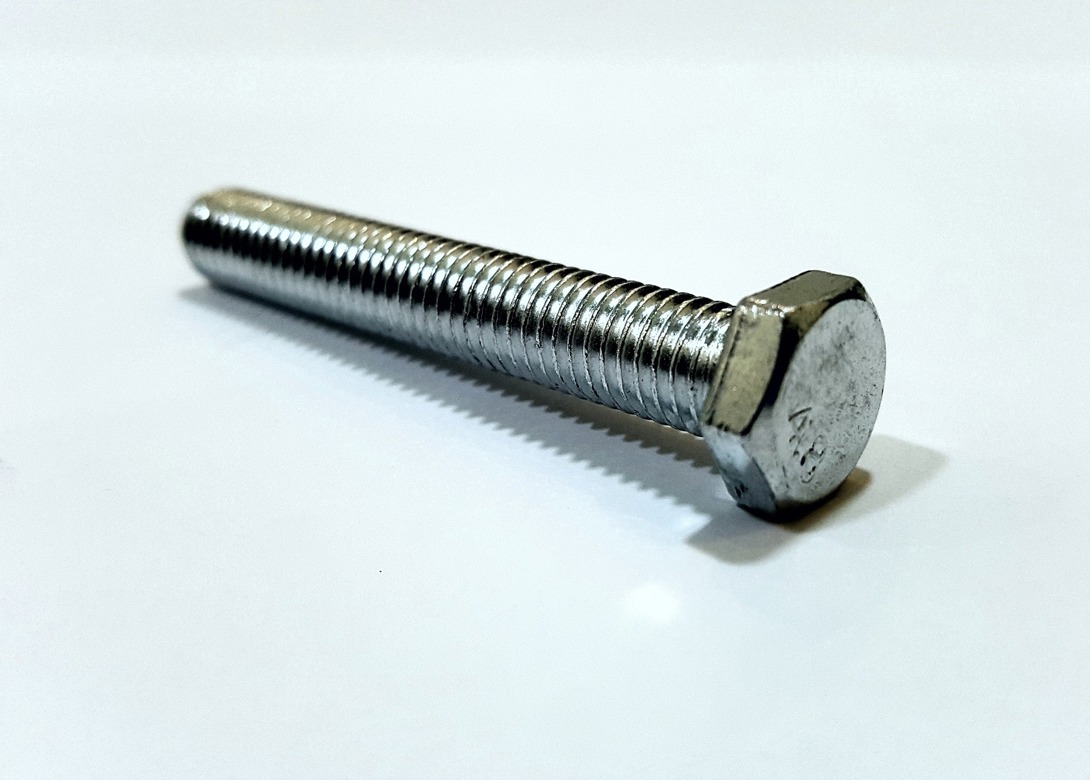
Figure One illustrates the terms L and D, so for example if an M10 bolt was used in a joint whose grip length is 40 then the L to D ratio is 40 / 10 = 4. One aspect of tightened bolts to appreciate is that the stretch of the bolt when fully tightened is relatively small. For example, an M10 bolt of property Class 8.8 when fully tightened in a joint whose thickness is 40mm will stretch about 0.1mm. The stretch is resisted by the bolt material producing the preload. This is important in that preload losses can occur in the joint subsequent to assembly.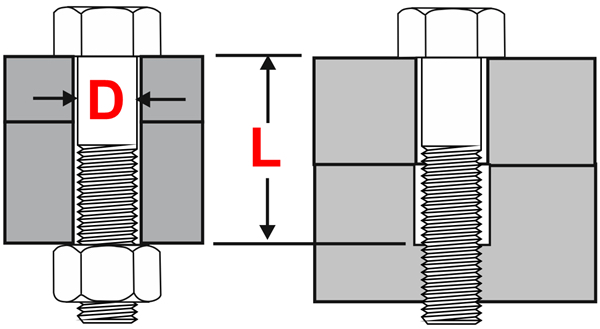
One type of preload loss is embedding. This is the collapse of the surface asperities between the joint interfaces and between the contact surfaces of the fastener. For the joint shown this loss would be in the order of 0.01mm to 0.02mm. The preload loss from embedding occurs when the joint sustains external loading. So, in this case the loss can amount to between 10% to 20% of the initial preload.
Now consider the two joints shown in Figure Two. Both bolts are the same size and strength and tightened to the same torque. Here the bolts are the same size but on one the grip length L, is half that of the other, say L is 40mm with the other 20mm. When both are tightened to the same torque value the bolt in the 20mm joint will stretch less, roughly, by half as much. (It is actually closer to 0.064mm due to some non linearity in the calculation).
So, when embedding loss occurs after the joint sustains external loading, a significantly larger loss in preload occurs, between 15% – 30% preload loss. For joints with a very low L/D ratio, comprising perhaps multiple layers of joint material, the preload loss from embedding can exceed 50%. Hence, the general rule of thumb, that joints with a large L/D ratio are to be preferred over those with a small L/D ratio. Many joints have an intrinsically small L/D ratio due to the nature of the parts being clamped. Putting spacers in the joint will increase the L/D ratio but packaging, weight, aesthetic, as well as cost limitations can preclude their use.
Conical washers are frequently used mitigate the effects of embedding loss on joints with small L/D ratios. The washers are thick Belleville washers that deflect under a compressive load. They are designed so they will fully compress at the target preload of the bolt. The deflection is relatively small, in the order of 0.3mm, but they significantly increase the stretch present in the bolt joint assembly. So instead of the 0.02mm being subtracted from the bolt stretch of 0.064mm, as in the previous example, with a single conical washer inserted under the bolt head, it would now be subtracted from 0.364mm. So subsequently the embedding loss would reduce the system’s deflection to 0.342mm, resulting in a preload drop of around 5%, compared to 15% to 30% without the washer.
The loss of preload from embedding being significantly reduced by the use of this type of washer in short grip length joints. Such washers are specified in DIN 6796 (conical spring washers for bolt nut assemblies).There is another advantage that long grip length ratios have over short; long grip length bolts are inherently more resistant to loosening than short bolts. Under small transverse joint movements, the bolt will bend rather than suffer slip of the head or thread bearing surfaces. The amount of joint movement needed to initiate slip of the bolt bearing surface is referred to as the ‘critical slip distance’.
www.boltscience.com
Having spent a decade in the fastener industry experiencing every facet – from steel mills, fastener manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, as well as machinery builders and plating + coating companies, Claire has developed an in-depth knowledge of all things fasteners.
Alongside visiting numerous companies, exhibitions and conferences around the world, Claire has also interviewed high profile figures – focusing on key topics impacting the sector and making sure readers stay up to date with the latest developments within the industry.





